Algorithm Characteristics and Properties
Definition
An Algorithm, which is a set of step-by-step instructions to complete a task, has several characteristics and properties that define the functioning and performance.
Explain Like I'm 5
Imagine you have a toy robot that can follow instructions to clean your room. The set of instructions it follows is like an algorithm. The way the robot performs - like how fast it cleans, how well it does the job, or how easy it is to fix if something goes wrong - those are its characteristics.
Digging Deeper
Each algorithm has certain characteristics that determine its suitability for a particular problem:
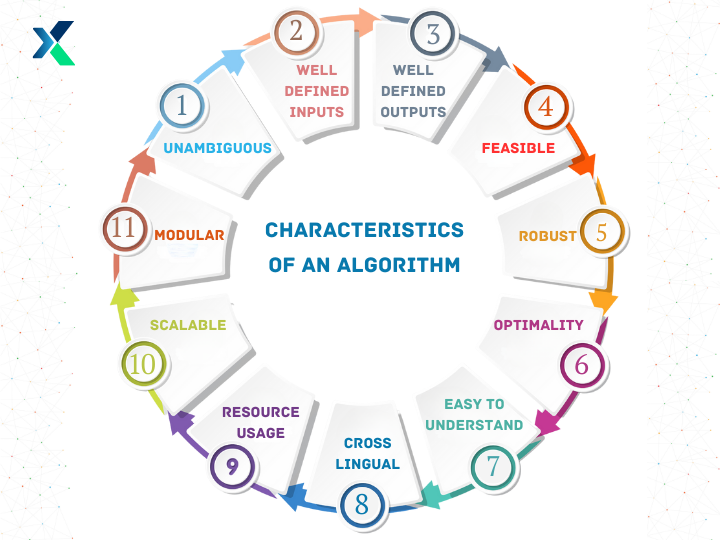
A characteristic of an algorithm refers to its inherent features or qualities that define its nature and functionality. These characteristics include:
-
Efficiency This refers to the resource usage of an algorithm. It can be measured in terms of time complexity (how long the algorithm takes to run) and space complexity (how much memory the algorithm uses).
-
Correctness This means that the algorithm produces the correct outputs for any given inputs.
-
Robustness A robust algorithm can handle erroneous or unexpected inputs gracefully.
-
Simplicity Simpler algorithms are generally easier to understand, implement, and maintain.
-
Unambiguous A key characteristic of the algorithm is that it should be precise and contain unambiguous instructions. Every step in the algorithm must be clearly defined and lead to a clear, single-defined meaning.
-
Well-defined Inputs An algorithm needs certain inputs to work on. These inputs should be well-defined so that the algorithm knows what to do with them.
-
Well-defined Outputs An algorithm must have a clearly defined output that it will yield. Once the program written based on it is executed, it should return at least one output (or more if required).
-
Feasible Ideally, an algorithm must be generic, simple, and understandable. It should also be practical so that it can be executed given the current available resources and technology.
-
Language Independent An algorithm should have a set of written instructions that can be implemented in any programming language and yield the same result regardless of the language in which it is written.
-
Optimality An algorithm operates in several types of complexity, such as time and space complexity. A must-have property of the algorithm is that it should return the best output given certain complexity criteria.
-
Understandable A major characteristic of the algorithm is that it should have well-defined steps that are logical and easy to comprehend, communicate, and organize.
-
Scalable Given the availability of big data and complex problems that require algorithms to process large inputs, an algorithm must be scalable without compromising its performance.
-
Resource Usage The algorithm must be optimized so that it smartly uses computer resources like CPU, GPU, memory, etc., and ideally consumes minimal resources for its work.
-
Robust An algorithm must deal with various inputs, such as outliers, missing values, and other anomalies, without returning incorrect results.
-
Modular An algorithm must have a design that can be decomposed into reusable components that can act as sub-algorithms. The algorithm's modular nature helps with its reusability and maintenance.

On the other hand, a property of an algorithm typically describes a specific attribute or behavior that can be observed or measured. Properties include:
-
Input An algorithm should be able to take zero, one, or more than one input.
-
Output At least one output should be able to be obtained from the algorithm.
-
Finiteness An algorithm must get terminated after following a finite time or executing a finite number of steps. Therefore, it should not run without an end or enter an infinite loop.
-
Effectiveness The algorithm must be effective, meaning it should be able to complete its objective and return the required output by following a finite number of steps.
-
Deterministic The user should be able to determine the algorithm's behavior and it should not work unexpectedly. Therefore, it should consistently produce the same result whenever the program written based on it is executed.